Gut Health and Mental Wellness: An Intricate Connection
Understanding the Gut-Brain Axis
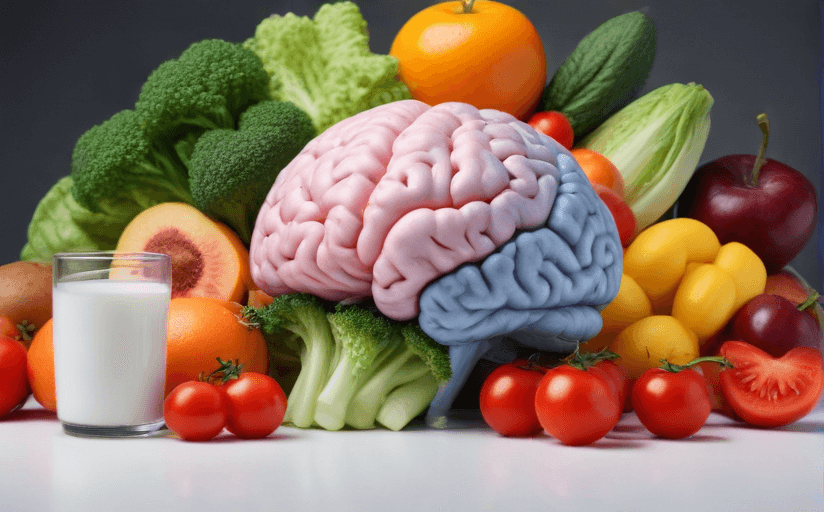
The complexities of our psychological make-up extend far beyond the brain. Science has recently uncovered a deep connection between our gut, also known as the 'second brain', and our mood, stress levels, and overall mental health. This relationship, known as the gut-brain axis, highlights the pivotal role that gut bacteria play in our mental wellness.
The Role of the Human Microbiome
The human gut is a host to trillions of bacteria -- collectively known as the microbiome. These bacteria have vital roles in digestion, immunity, and even the production of essential vitamins. Recent research has unveiled that they also communicate with our brain through a variety of pathways, influencing our emotions and behaviour.
Gut Bacteria: Affecting Mood and Mental Health
Scientists have found a strong correlation between the types of bacteria present in the gut and an individual's mental health. Certain strains of bacteria, such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium, are found in lower concentrations in individuals suffering from mood disorders like depression and anxiety. These bacteria are thought to influence the production of serotonin, a neurotransmitter that regulates mood, among other things.
Impacts on Mental Health
Disruptions in the composition and diversity of the gut microbiome, often caused by factors like stress, poor diet, or antibiotics, can lead to 'dysbiosis'. This has been linked to a host of mental health conditions such as depression, anxiety, and even more severe neurological disorders like Autism and Alzheimer's disease. However, more research is required to fully understand these connections and develop potentially effective therapeutic strategies.
Improving Gut Health to Enhance Mental Wellness
A growing body of evidence suggests that modifying our diet and lifestyle could positively influence our gut health and, by extension, our mental wellness.
Dietary Changes
A diet rich in fiber and fermented foods, for example, can support the growth of beneficial bacteria in the gut. These foods include fruits, vegetables, whole grains, yogurt, and other probiotic-rich foods. Limiting intake of processed foods and those high in sugar also contributes to a healthy gut.
Probiotic Supplements
Probiotic supplements, which contain beneficial bacteria, can also boost gut health. However, they should be used under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Conclusion: The Future of Gut Health and Mental Wellness
As we continue to explore the complex relationship between the gut and the brain, the future of mental health treatment and prevention appears increasingly intertwined with our understanding of the microbiome. Evidence supporting the gut-brain axis theory is building, paving the way for exciting new therapies to enhance both gut and mental health. However, it is equally crucial to maintain a balanced diet, regular exercise, and good sleep hygiene for optimal health and wellbeing.















Comments
Leave a Comment