Impact of Climate Change on Biodiversity
Understanding Climate Change
Climate change refers to the significant alterations in global weather patterns over a prolonged period. The consensus among scientists is that the Earth's climate is rapidly changing due to anthropogenic activities, primarily the burning of fossil fuels leading to a sharp increase in greenhouse gases in Earth's atmosphere.
Climate Change and Biodiversity Loss
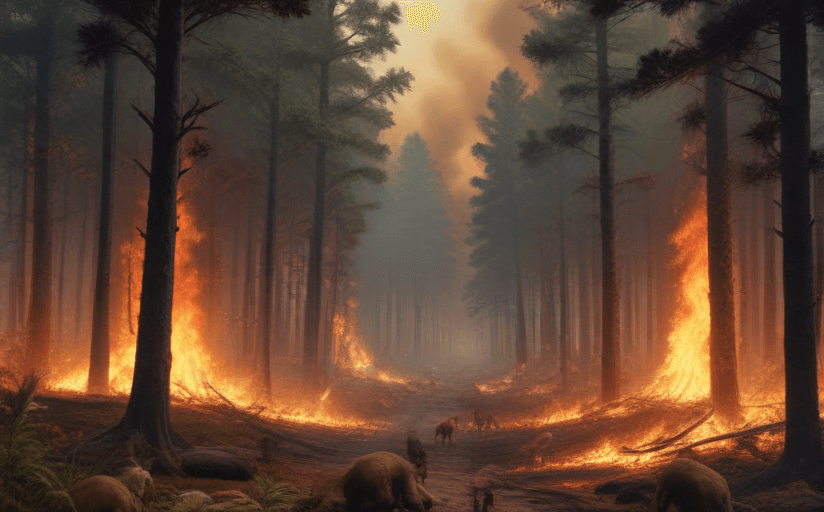
Climate change has a direct and profound impact on biodiversity. The rapid shifts in climate conditions stress ecosystems and threaten biodiversity. These effects are seen through changes in species distribution, population sizes, and the timing of reproduction or migration events, as well as an increased rate of disease in plants and animals.
The Impact on Global Ecosystems
The impact of climate change on biodiversity is not uniform. Some areas and ecosystems are hit harder than others. Tropical regions, for example, which are home to the majority of the world's biodiversity, are also the places where species are most vulnerable to climate change. In contrast, areas like the Arctic are warming at a rapid pace, causing rapid loss of glaciers and sea ice, and thereby threatening the species adapted to these conditions.
Vulnerable Species
Climate change is selective, and certain species are more vulnerable than others. Polar bears, coral reefs, and amphibians are among the most impacted by climate change. Polar bears rely on sea ice for hunting, but as the Arctic warms, the ice shrinks, leaving polar bears with a declining food source. Similarly, warmer sea temperatures cause massive coral bleaching events, threatening a wide array of marine biodiversity. And for amphibians, subtle changes in temperature can impact their sensitive life cycles.
Case Studies
Case studies, scientific reports, and expert opinions strongly validate the effects of climate change on biodiversity. In Australia, the Great Barrier Reef experienced the worst recorded coral bleaching event in 2016 due to warmer ocean temperatures. In the Arctic, reports suggest a 40% decline in polar bear populations over the past decade because of melting sea ice.
Potential Mitigation Measures
Combating the impact of climate change on biodiversity requires significant and urgent efforts at all levels. Reduction in greenhouse gas emission, advancing renewable energy technology, minimizing habitat destruction, and investing in conservation efforts are all key elements in mitigating these impacts.
Roles of Individuals, Communities and Government Policies
The battle against climate change and biodiversity loss is one that must be fought on all levels. Individuals can influence biodiversity by consuming responsibly, reducing waste, and planting native plants. Communities can organize conservation efforts, establish protected areas, and implement sustainable practices. At the highest level, governmental policies should aim for nature conservation while fulfilling societal needs, facilitate transitions to renewable energy, and enforce regulations that protect habitats from various pressures including climate change.
Conclusion
Climate change is a driving force behind the current loss of biodiversity, threatening species survival and ecosystem health. However, by understanding this dynamic and taking appropriate measures at all levels of society, we can help to mitigate these effects and uphold the diverse richness of life on Earth.












Comments
Leave a Comment