The Role of Fungi in Nature's Complex Ecosystem
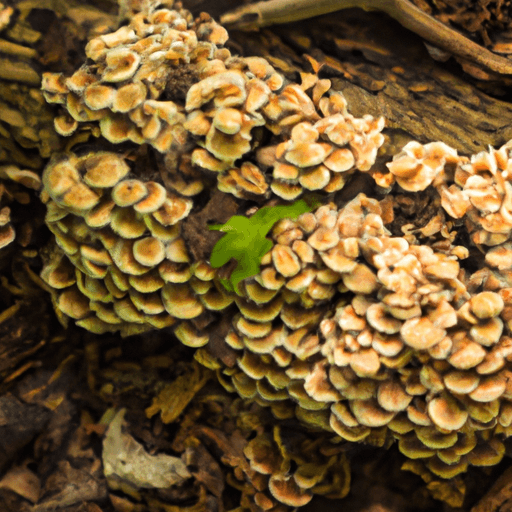
Fungi, often overlooked and misunderstood, play crucial roles in nature's complex ecosystems. They form symbiotic relationships, contribute to nutrient cycles, help in soil stabilization and significantly affect both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems.
Symbiotic Relationships of Fungi
Fungi form symbiotic relationships with a variety of organisms, from plants to insects. The most common type is the mycorrhizal association where fungi colonize the roots of plants, increasing their water and nutrient uptake. In return, the fungi obtain sugars and other organic compounds from the plants. Fungi also form mutualistic relationships with insects. For example, leaf cutter ants propagate certain types of fungi, which they feed with leaves they collect. In return, these fungi serve as a primary food source for the ant colonies.
Contribution to Nutrient Cycles
Playing an integral part in the nutrient cycle, fungi are primarily decomposers. They break down complex organic materials, such as dead plant matter, into simpler compounds. This nutrient recycling process replenishes the soil with essential elements that plants can use to grow. The breakdown of dead material also promotes soil health, including its texture and structure.
Fungi and Soil Stabilization
Fungi, specifically mycorrhizal fungi, contribute significantly to soil stabilization by forming extensive networks called mycelium. These networks not only help in the nutrient and water absorption but also act as a glue that holds soil particles together. This process contributes significantly to preventing soil erosion.
Fungi in Terrestrial and Aquatic Ecosystems
Fungi contribute to terrestrial ecosystems by decomposing organic matter, forming symbiotic relationships, and soil stabilization. In aquatic ecosystems, they serve a similar role by helping remove pollutants from the water through a process known as mycoremediation and play a part in the food chain serving as food for many aquatic organisms.
Negative Impacts of Fungi
Despite numerous positive impacts, fungi can also negatively affect the environment. When out of balance, such as the rampant spread of pathogenic fungi, they can cause devastation in ecosystems. These fungi cause diseases in plants and animals, leading to massive die-offs, disrupting ecological balance, and potentially leading to extinction events. Also, some fungi can produce harmful toxins, affecting the health of other species.
Recent Findings
Recent studies have emphasized the critical role fungi play in maintaining ecological balance. One study found that decline in fungal diversity might have severe implications for forest health and agricultural productivity. It stresses the importance of conserving fungal diversity to ensure the overall health of ecosystems.
In conclusion, fungi play a multi-faceted role in our ecosystems as partners, recyclers, protectors, and sometimes, as challengers. Understanding their complex nature and preserving their diversity is integral to maintaining ecological balance.














Comments
Leave a Comment