Exploring How Human Activity Has Changed Animal Behavior
Human activity has changed the behavior of animals in a variety of ways, from direct displacement and disruption of habitats, to the introduction of foreign species, and other human-driven environmental changes. This has created a range of challenges for animals, with potentially short-term and long-term consequences to animal populations. In this article, we will explore how human activity has changed animal behavior, and the challenges and consequences these changes bring.
Disruption of Habitats
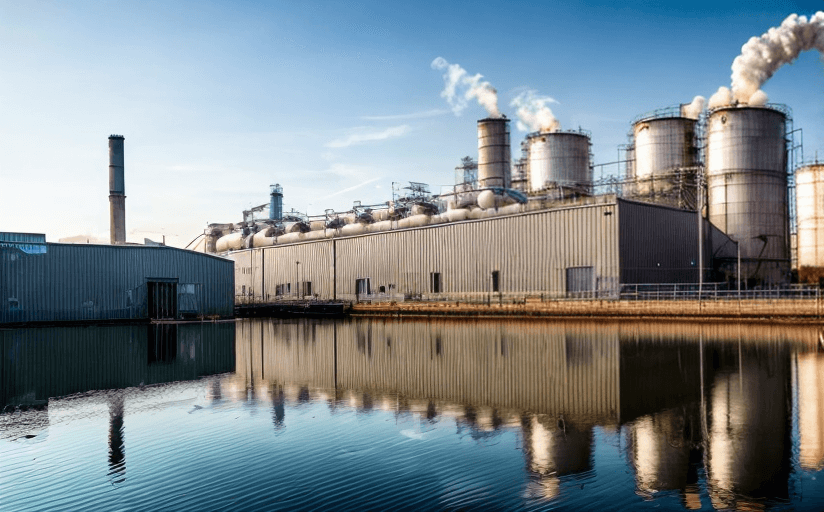
The most direct way human activity has changed animal behavior is through the disruption of habitats. This includes activities such as deforestation, urbanization, and infrastructure development. As habitats are destroyed, animals are forced to relocate or adapt to the changes in their environment. This can lead to a range of stressors for animals, including increased competition for resources, changes in prey availability, and disruption of normal mating or migration patterns. These changes can have serious consequences for animal populations, as they may not be able to adapt quickly enough to survive.
Introduction of Foreign Species
Another way human activity has changed animal behavior is through the introduction of foreign species. This can occur through intentional or accidental introductions, either through purposeful introductions for the pet trade, or through accidental introductions through human activities such as shipping and travel. Introducing foreign species to an ecosystem can cause a variety of changes, from competition for resources to the spread of diseases. These changes can have serious consequences for native species, which may not have evolved to cope with the new species.
Other Human-Driven Environmental Changes
Human activity also drives a range of other environmental changes, from pollution to climate change. These changes can have a significant impact on animal behavior, as animals may be forced to adapt to the new conditions or face extinction. For example, climate change can cause shifts in the range of species, leading to competition for resources, changes in prey availability, and disruptions to mating or migration patterns.
Challenges and Consequences
The changes in animal behavior due to human activity create a range of challenges and potential consequences for animal populations. In the short term, animals may be forced to adapt to the changes in their environment, leading to increased competition for resources, changes in prey availability, and disruption of normal mating or migration patterns. In the long term, these changes can have serious consequences, as animals may not be able to adapt quickly enough to survive. Furthermore, the introduction of foreign species can have serious consequences for native species, as they may not have evolved to cope with the new species.
Conclusion
Human activity has changed the behavior of animals in a variety of ways, from direct displacement and disruption of habitats, to the introduction of foreign species, and other human-driven environmental changes. These changes create a range of challenges for animals, with potential short-term and long-term consequences to animal populations. It is important that we continue to take steps to manage and reduce the impact of human activity on animal behavior, in order to protect and conserve animal populations for future generations.













Comments
Leave a Comment