The Mental Benefits of Exercise
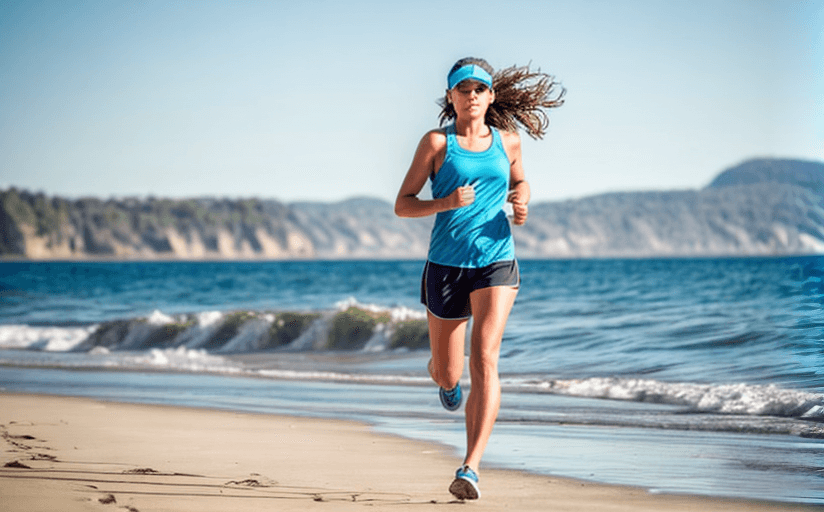
Exercise has long been associated with physical health benefits, such as improved cardiovascular health and weight loss. But there are also important mental benefits of exercise, such as reducing stress and anxiety, improving mood and self-confidence, and building resilience. This article will explore the scientific evidence that supports these claims and the ways in which exercise can improve mental wellbeing.
Reducing Stress and Anxiety
Regular exercise has been shown to reduce stress and anxiety by increasing the release of endorphins, which are the body’s natural feel-good hormones. Exercise also reduces levels of the stress hormone cortisol, which can have a calming effect on the body and mind. Studies have found that regular exercise can be as effective as medication for reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression, making it an important tool for managing mental health.
Improving Mood and Self-Confidence
Exercise has also been found to have a positive effect on mood and self-confidence. Research has shown that regular physical activity can improve mood, reduce feelings of depression and anxiety, and improve self-esteem. Exercise also releases endorphins, which can lead to an improved sense of wellbeing and happiness.
Building Resilience
Exercise can also help to build resilience, which is the ability to cope with difficult situations. Studies have found that regular physical activity can help to reduce levels of stress, anxiety, and depression, making it easier to cope with difficult life events. Exercise can also help to improve mental clarity and focus, which can assist with problem-solving and decision-making.
In conclusion, the scientific evidence is clear: regular exercise can have significant benefits for mental health, such as reducing stress and anxiety, improving mood and self-confidence, and building resilience. It is an important tool for maintaining mental wellbeing and should be included in any mental health plan.
















Comments
Leave a Comment