Human Activity and Climate Change: Exploring the Physical and Social Implications
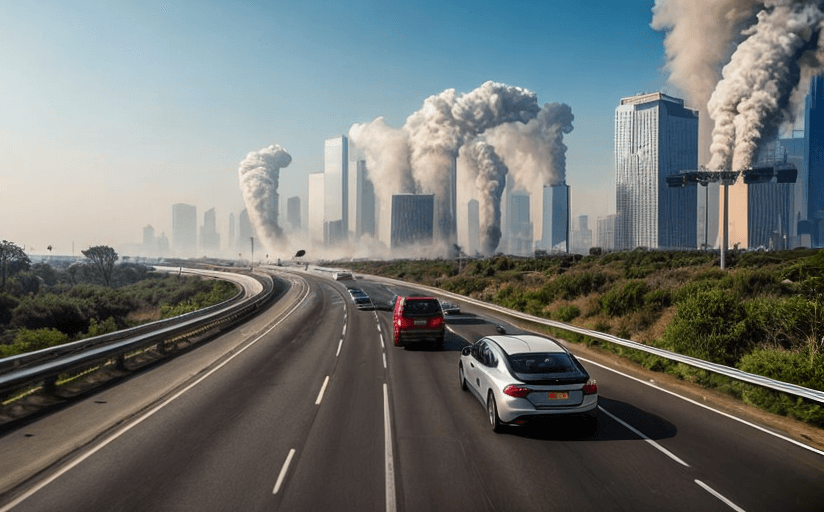
The effects of human activity on climate change are becoming increasingly evident. From the melting of polar ice caps to more frequent and intense extreme weather events, the environmental impacts of human activity are becoming increasingly clear. The most significant contributions of human activity to climate change include burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and agricultural activities. In order to mitigate these effects, individuals and governments must take action to reduce their environmental footprint. In this article, we will explore the physical and social implications of human-caused climate change, and discuss strategies for action.
The Physical Impacts of Human Activity on Climate Change
The most significant human contribution to climate change is burning of fossil fuels. The burning of fossil fuels, such as coal and oil, releases large amounts of greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, into the atmosphere. As these gases accumulate in the atmosphere, they trap heat, causing an increase in global temperatures. In addition to burning of fossil fuels, human activities such as deforestation and agricultural activities also contribute to climate change. Deforestation removes trees that would otherwise absorb carbon dioxide from the atmosphere, while agricultural activities such as livestock farming produce large amounts of methane.
The Social Implications of Human-Caused Climate Change
The physical impacts of climate change have far-reaching social implications. As global temperatures continue to rise, sea levels will continue to rise, leading to increased flooding and coastal erosion. This, in turn, will lead to displacement of communities and loss of wildlife habitat. In addition, extreme weather events, such as droughts and heat waves, will become more frequent and intense, leading to disruption of food and water supplies and increased risk of disease. Finally, climate change will also lead to increased economic costs, as communities are forced to adapt to the impacts of climate change.
Strategies for Action
In order to mitigate the effects of climate change, it is essential that individuals and governments take action to reduce their environmental footprint. On an individual level, individuals can reduce their carbon footprint by making simple lifestyle changes, such as switching to renewable energy sources for power, eating less meat, and reducing their reliance on cars. Governments can also take action to reduce their environmental footprint by investing in renewable energy sources, passing laws to protect forests, and encouraging sustainable agricultural practices. Finally, governments can also work together to develop international agreements, such as the Paris Climate Agreement, to reduce emissions and protect the environment.
Conclusion
The effects of human activity on climate change are becoming increasingly evident. Burning of fossil fuels, deforestation, and agricultural activities are the most significant contributions of human activity to climate change. In order to mitigate these effects, individuals and governments must take action to reduce their environmental footprint. By making simple lifestyle changes, investing in renewable energy sources, and developing international agreements, individuals and governments can take action to reduce their environmental footprint and mitigate the effects of climate change.














Comments
Leave a Comment