Cooking for Space Travel: Nutrition, Challenges, and Innovations
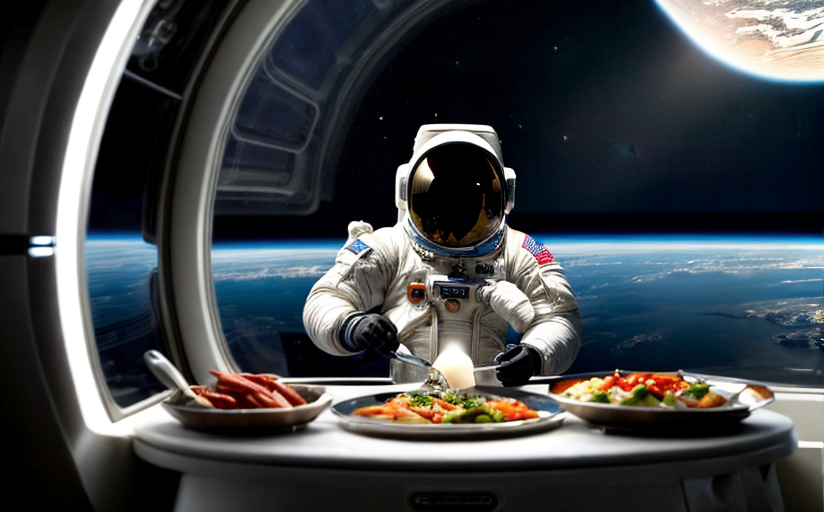
The introduction of humans into space brought with it a unique challenge - how do we cook for astronauts? The importance lies not in the act of cooking itself, but rather in providing astronauts with the necessary nutrition in a form that they can consume comfortably in a microgravity environment. The difference in gravity fundamentally differentiates the food designed for space from that on Earth.
Nutrition Requirements for Astronauts
The nutrition required by astronauts must take into account a range of factors. These include durability to withstand travel, the lightness of weight, the issues around microgravity, and minimal waste generation. Astronauts also require more quantities of certain nutrients like vitamin D, due to limited exposure to the sunlight and calcium for bone health as they face bone density loss in the space environment. Any food designed for space must be capable of providing all these nutritional requirements whilst also being palatable for the crew.
Challenges in Creating Meals for Space
There are notable challenges to producing food that can withstand the rigors of space travel and still maintain its nutritional and taste value. Maintaining a long shelf life is one of the key challenges faced by developers, especially for long-endurance missions. The food also needs to maintain its taste over time, which can be difficult to achieve given the constraints of packing and storage.
Innovative Solutions in Space Food
In facing these challenges, scientists and researchers have come up with an array of innovative solutions. Some of these include preserving food through dehydration, using thermostabilization, and developing food bars specifically designed to provide the necessary nutrition. Current research also explores the possibility of growing food in space, which can help provide fresh produce for astronauts and manage waste effectively.
The Future of Space Food
The future of astronaut food lies with cutting-edge technologies such as 3D printing meals and advancements within astrobiology. These could include cultivating microorganisms that can process inedible biomass into nutritious food. Other future directions could include the development of self-growing food, akin to a 'Martian Garden' and creating food sources from CO2 through chemical reactions.
Conclusion
As humanity continues to march towards a future that includes more extensive space exploration, the question of how to provide sustainable food solutions for astronauts remains a present and urgent query. It can be stated with certainty that the continued development and innovation in the field of space food will have a profound impact on the future of space travel.

















Comments
Leave a Comment