An In-Depth Analysis of the Importance and Impact of Gut Health on Mental Wellbeing
Introduction
The human body is host to trillions of bacteria, fungi, viruses, and parasites, collectively known as the microbiota, with the gut being the largest residence. Our gut microbiota plays a crucial role in facilitating fundamental physiological processes, affecting not only our physical but also our mental wellbeing. This article aims to dissect the intricate relationship between the gut and the brain, the importance of maintaining a balanced gut microbiome, and how it significantly influences our mood, stress levels, anxiety, and overall mental health.
The Gut-Brain Connection
The gut and the brain might seem entirely distinct entities, but they are linked by a sophisticated network of nerves, hormones, and components of the immune system. This is often referred to as the gut-brain axis. A key part of this network is the vagus nerve, the longest cranial nerve in the body, serving as a two-way information highway between the gut and the brain. This neurohumoral communication pathway allows gut microbes to influence brain chemistry and behavior, manifesting in various aspects of mental wellbeing.
The Relevance of a Balanced Gut Microbiome
A healthy gut microbiome significantly contributes to a well-functioning brain, sculpting our neural development, influencing behavior, modulating mood, and managing the body's response to stress. Imbalances in the gut’s microbiota, known as dysbiosis, can lead to mental health issues such as anxiety, depression, and stress disorders.
Emerging research has begun to elucidate the mechanisms behind these effects, suggesting that gut bacteria can produce neurotransmitters and neuromodulators, such as serotonin, dopamine, and gamma-aminobutyric acid, all of which play pivotal roles in mood and overall brain health. Hence, sustaining a balanced gut microbiota is instrumental for mental wellbeing.
The Role of Nutrition and Lifestyle
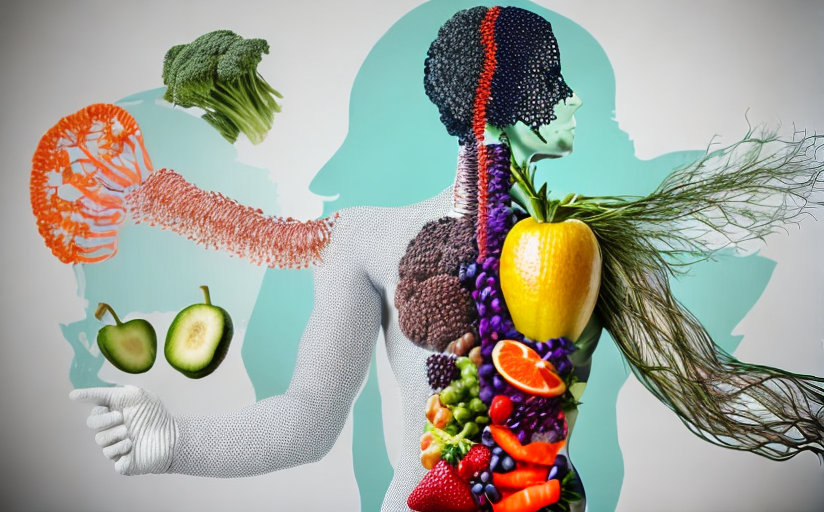
Maintaining gut health is closely linked to our dietary and lifestyle choices. A diverse diet rich in fiber, lean proteins, healthy fats, and probiotics promotes a more diverse gut microbiome, which is associated with better mental health. Regular physical activity, adequate sleep, stress management, and minimal alcohol intake are all crucial for maintaining a healthy gut, thus positively affecting our mental wellbeing.
Practical Advice
Simple lifestyle modifications can have a profound impact on gut health. This includes introducing more probiotic-rich foods like yogurt, kefir, and fermented foods into your diet, increasing fiber intake through fruits, vegetables, and whole grains, and performing regular physical activities. It is also essential to hydrate adequately, limit processed foods, and maintain a regular sleep pattern.
Recent Research Findings
Recent scientific studies continue to reaffirm the intricate relationship between gut health and mental wellbeing. One such study in 2019 found that individuals with certain types of gut bacteria had different brain structures, thereby affecting an individual's mood and behavior. Similarly, a 2020 study found that dietary interventions promoting a healthy gut microbiome significantly improved symptoms in patients with major depressive disorder, illustrating the strong and necessary link between gut health and mental wellbeing.
Conclusion
The multifaceted nature of the gut-brain connection is ongoing, and the field continues to grow and evolve. The crucial role gut health plays in mental wellbeing emphasizes the need for a holistic health perspective focusing on both physiological and psychological health. Thus, nurturing our gut health should be a core element in promoting mental wellbeing.














Comments
Leave a Comment