All About Bioluminescence
Bioluminescence, a fascinating natural phenomenon, is the ability of organisms to produce light through a series of biochemical reactions. Although it seems otherworldly, bioluminescence is a survival strategy evolved over millions of years, serving vital roles in ecosystems across the globe.
The Science Behind Bioluminescence
Bioluminescence involves a reaction between a light-producing molecule called luciferin and an enzyme, luciferase. This reaction results in the emission of light without the generation of substantial heat, a phenomenon known as 'cold light'. In some organisms, bioluminescence originates from symbiotic bacteria that produce light.
Functions of Bioluminescence
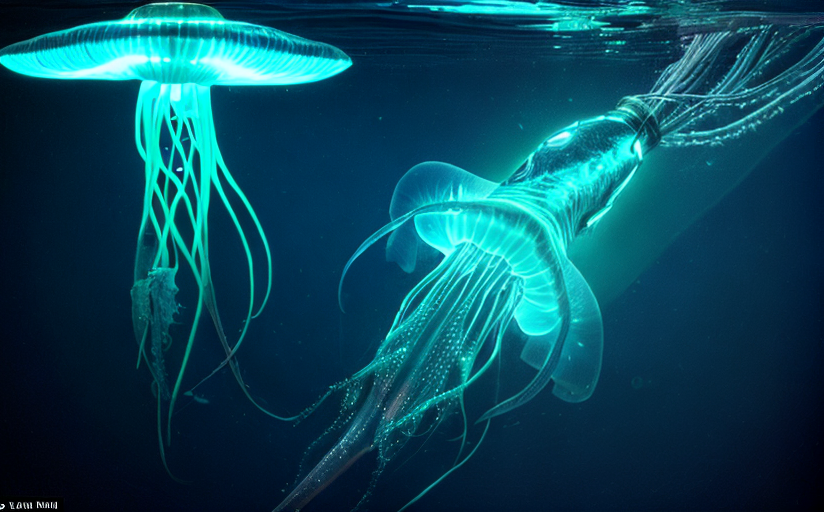
Bioluminescence serves diverse functions, including mate attraction, predation deterrent, and communication. Organisms in the pitch-black depths of the ocean use light-producing capabilities to lure or confuse potential prey and evade predators. They also communicate via light signals, illuminating the rich complexity of life beneath the ocean surface.
Species Exhibiting Bioluminescence and Their Habitat
Bioluminescent organisms span several taxa, from bacteria and fungi to insects and marine creatures. Fireflies, glow worms, certain squid, and fish species are well-known bioluminescent organisms. This phenomenon is mainly observed in marine habitats, notably in the twilight zone of the ocean, where sunlight is unable to penetrate.
Bioluminescence and Ecosystem Dynamics
Bioluminescence significantly influences ecosystem dynamics. It contributes to food web dynamics by aiding predation and evasion, and by facilitating intra- and interspecies communication, it indirectly shapes species distribution and biodiversity patterns. Research links bioluminescence with biodiversity protection, suggesting that bioluminescent capabilities may correlate with better survival rates in hostile environments.
Threats to Bioluminescent Species
Like numerous species worldwide, bioluminescent organisms also face a variety of threats. Climate change, ocean acidification, pollution, and habitat destruction pose significant risks, impacting the delicate balance of ecosystems. If bioluminescent species populations diminish, there could be dramatic shifts in food web dynamics and ecosystem health.
Conclusion
Bioluminescence, much more than a visual spectacle, is an evolved adaptation that significantly affects ecosystem dynamics and biodiversity. We have much more to learn from this natural wonder. As we do, it is paramount that we work to mitigate the threats bioluminescent species face to preserve the mesmerizing diversity of life on our planet.
















Comments
Leave a Comment