The Impact of Vaccination on Public Health
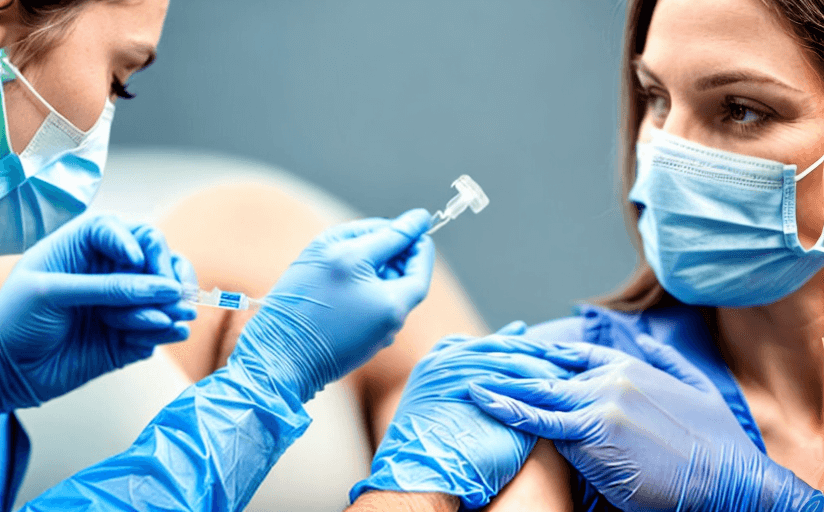
Vaccinations are an integral part of public health, playing an undeniable role in minimizing the impact of infectious diseases. This article focuses on the in-depth examination of the impact HPV vaccines have on individual and public health.
Overview of Vaccinations
Vaccines help prepare individuals’ immune systems to fight off pathogens efficiently. This immunization process is mainly achieved by injecting weakened or dead versions of pathogens, or parts of pathogens. This provokes the immune system to fight off the pathogen, creating antibodies and memory cells that can speed up the defensive process if the person encounters the same disease later in life. The pivotal role of vaccines lies in their ability to prevent the outbreak of potentially deadly diseases.
Commonly Administered Vaccines and Their Effects
There are a wide variety of vaccines including live-attenuated vaccines, inactivated vaccines, subunit vaccines, toxoid vaccines, and conjugate vaccines. These vaccines help protect against diseases such as measles, mumps, rubella, polio, hepatitis, HPV, influenza, pneumococcal disease, and more. While short-term side effects of vaccines may include mild fever and soreness at the injection site, their longer-term benefits far outweigh these minor discomforts.
The Role of Vaccination in Infectious Disease Prevention
Vaccinations have proven to drastically decrease the incidence and severity of numerous infectious diseases. Globally, vaccines prevent approximately 2 to 3 million deaths each year —a figure that could further increase with optimized vaccine coverage. Notably, vaccines have eradicated smallpox and significantly limited the prevalence of other diseases such as measles, mumps, and polio.
Impact of Immunization
Immediate Impact
Vaccination results in immediate immunity against specific diseases, reducing the burden on the healthcare system due to reduced incidence of disease outbreaks, hospitalizations, and deaths.
Long-term Impact
Long-term benefits of vaccination include the eradication of diseases, improved life expectancy, and increased productivity due to reduced illness. Widespread immunization can also lead to herd immunity, protecting even those who are unvaccinated by reducing the overall prevalence of the disease within a population.
Health, Economic, and Societal Benefits of Vaccination
Vaccination contributes significantly to public health by reducing the spread of infectious diseases, leading to healthier, longer lives. The economic benefits of vaccination cannot be overlooked as it reduces healthcare costs associated with treating diseases. Societally, vaccination helps maintain economic productivity by reducing the number of people suffering from preventable diseases.
Controversies and Challenges
Despite the proven benefits of vaccines, vaccine hesitancy and accessibility remain significant challenges. Misinformation, lack of trust in health systems, fear of side-effects, and geographical barriers can lead to reduced vaccination rates, thereby threatening public health.
Solutions
Potential solutions may include targeted education campaigns, improving vaccine accessibility in remote areas, ensuring vaccine affordability, and implementing policies to hold misinformation-spreading parties accountable.











Comments
Leave a Comment