Is Nuclear Energy a Sustainable and Safe Solution to the Climate Crisis?
With a mounting climate crisis on our hands, the search for alternative, renewable and low-carbon energies has taken precedence. Among them, nuclear energy draws significant attention, and its efficacy as a long-term solution is a frequent subject of contention.
The Case for Nuclear Energy
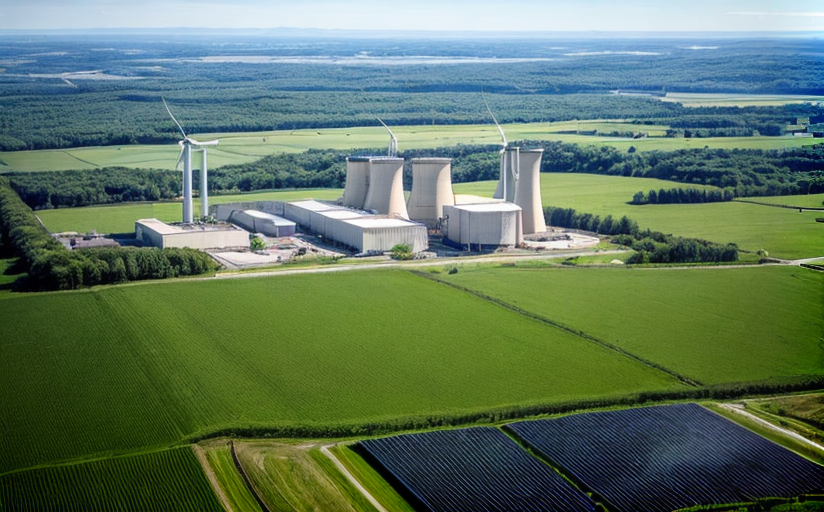
The primary appeal of nuclear energy lies in its large power generation capability and low GHG (Greenhouse Gas) emissions compared to traditional fossil fuels. Some experts argue nuclear energy's carbon footprint is comparable to wind and solar power, making it a potential candidate for combating the climate crisis.
Additionally, nuclear power boasts of remarkable 'energy density' - a small amount of nuclear fuel can produce substantial energy, promising a resource-efficient solution.
Safety Concerns and The Question of Nuclear Waste
Critics of nuclear power often highlight safety as a major concern. Events such as the Chernobyl and Fukushima accidents amplify this worry. While it's true that advancements in nuclear technology have drastically improved safety protocols and standards, the risk cannot be entirely eliminated.
Furthermore, the issue of nuclear waste is a significant argument against nuclear power. Spent nuclear fuel is extremely hazardous, and there is no universally agreed upon long-term storage solution. To add to public anxiety, inadequate disposal can lead to serious environmental and health consequences.
Comparative Sustainability
Comparisons with other renewable sources demonstrate nuclear power is not the most sustainable option. Solar, wind, and hydropower energy sources have more favorable life cycle assessments and require less water. However, they also require large tracts of land and can be subject to fluctuations in availability due to weather conditions, a weakness not shared by nuclear energy.
The Final Analysis
The question of nuclear energy being a sustainable and safe solution to the climate crisis is multifaceted. Nuclear power's striking energy density and low carbon emissions present it as an attractive strategy in battling global warming. Yet glaring safety concerns and the unresolved issue of nuclear waste management tend to overshadow these benefits.
Ultimately, more extensive research and a holistic, realistic approach are vital for leveraging nuclear energy in addressing climate issues. Nuclear power is certainly a critical piece of the decarbonization puzzle; however, its promotion should not overshadow or cease development and investment in other renewables.
References
List your references here, formatted according to your chosen citation style.














Comments
Leave a Comment