The Contributions of Fungi to Ecosystem Sustainability
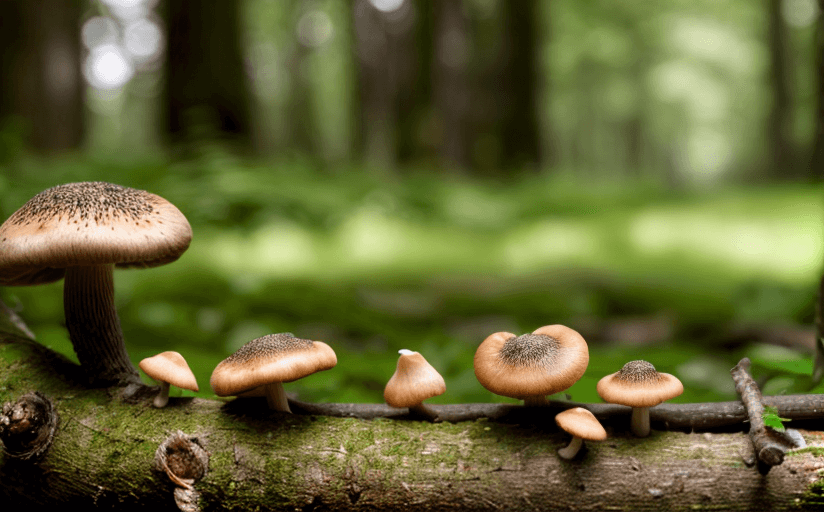
Fungi, a vastly diversified kingdom in nature, bear immense significance in the mechanics of ecosystem sustainability. Their functionality in natural habitats goes beyond what meets the eye; they play pivotal roles in decomposition, nutrient cycling, and symbiotic relationships with plants and animals, contributing largely to the healthiness of the ecosystem.
The Roles of Fungi in the Ecosystem
Decomposition and Nutrient Cycling
Fungi function as nature's decomposers by breaking down organic material such as dead plants and animal matter. Through the process of decomposition, fungi convert complex organic material into simpler compounds, thereby enabling the recycling of nutrients in the ecosystem. This role is essential for maintaining the flow of nutrients and energy within an ecosystem, driving core processes for other living organisms.
Symbiotic Relationships with Plants and Animals
In addition to decomposition, fungi engage in mutualistic symbiotic relationships with many plants and animals. Mycorrhizal fungi, for example, form symbiotic relationships with plant roots, providing the plants with essential nutrients while receiving sugars in return. Such partnerships, known as mycorrhizae, are vital to the survival of various plant species. Similarly, fungi contribute to the survival and wellbeing of many animal species too. For instance, some animals rely on fungi for food, while others use them for shelter or reproduction.
The Contribution of Fungi to Ecological Balance and Sustainability
The activities of fungi contribute significantly to maintaining ecological balance and sustainability. Their substantial role in recycling nutrients ensures the continual productivity of ecosystems. Furthermore, mycorrhizal associations can enhance plant resistance to diseases and environmental stresses, promoting plant diversity and overall ecosystem resilience.
Potential Detrimental Effects of Fungi
Despite their invaluable contribution to the ecosystem, fungi can also have detrimental effects under certain conditions. Some species of fungi are pathogens that can cause diseases in plants and animals, threatening biodiversity. Also, extreme growth of saprophytic fungi, which feed on dead organic material, can lead to swift depletion of organic matter, upsetting the natural nutrient cycle.
Clearly, though they might be overlooked, fungi play crucial roles in nurturing life on Earth. Understanding the dimension of their influence, definitely deepens our comprehension of ecosystem functionings and inspires further research into their potential applications for a sustainable future.












Comments
Leave a Comment