Genetically Modified Foods: Pros and Cons for Health and Environment
Genetically modified (GM) foods continue to generate robust debates in the spheres of science, health and environment. As we delve into this topic, we aim for a balanced view that illustrates both the benefits and drawbacks of these foods in our health and environment.
The Science of Genetically Modified Foods
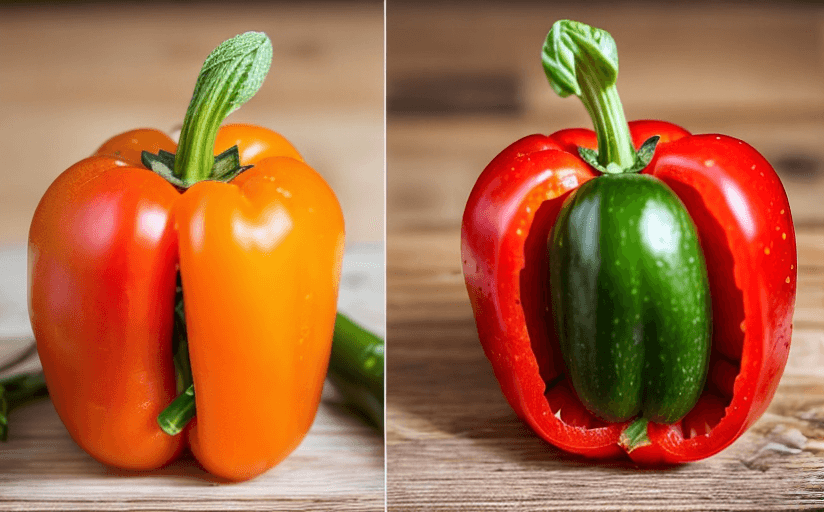
The process of creating GM foods involves altering the DNA of a plant or animal. This is achieved through the introduction of genes from other species to boost the organism's characteristics such as disease resistance, pest resistance, and overall yield. These genetic alterations can produce larger fruits, vegetables, and meat products, while also making them more robust against various adverse environmental conditions.
The Relevance of GM Foods in Today's Society
Modern society continues to face the ongoing challenge of a rising global population and climate change. Through genetic modification, we can increase yield and make crops more resistant to changing weather patterns, thus ensuring the world's food supply meets its demand.
Current Examples of GM Foods
Today, GM foods are commonplace in our grocery stores. Some of the most common examples include corn, soya, potatoes, and papaya. These foods have been genetically engineered for disease resistance, increased yield, and enhanced nutritional value.
Health Benefits and Risks
GM foods have potential health benefits. For instance, they can be fortified with essential nutrients such as vitamins and minerals to fight malnutrition. Golden Rice, rich in vitamin A, is an example. However, critics argue that genetically modified foods may pose health risks. They point out potential allergic reactions, antibiotic resistance, and the possibility of unknown health effects due to the manipulation of an organism's genetic structure.
Environmental Advantages and Challenges
In terms of environmental benefits, GM crops can withstand adverse weather conditions and resist pests and diseases, reducing the need for chemical pesticides and fertilisers. This can lead to less environmental pollution and lower greenhouse gas emissions. Conversely, the introduction of GM species to the environment could disrupt ecosystems and lead to a loss of biodiversity. There are also concerns about the increased use of herbicides linked to herbicide-resistant GM crops, which can negatively impact the environment.
Conclusions
Scientific research into the health implications and environmental effects of genetically modified foods is ongoing. It will help us understand the long-term consequences better. Current knowledge suggests a mixture of both advantages and potential drawbacks, highlighting the need for rigorous evaluation and careful oversight in the deployment of this technology.














Comments
Leave a Comment