Insects and The Future of Sustainable Cooking and Diets
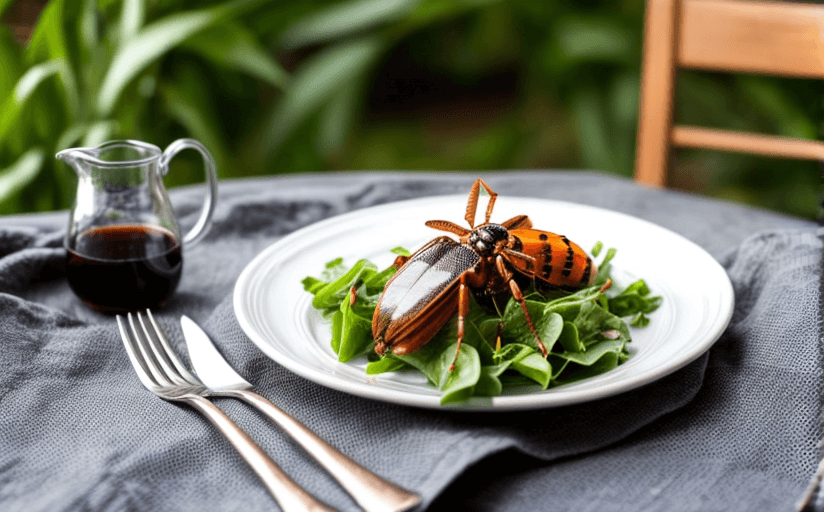
In the face of pressing environmental issues like climate change and mounting food shortages, there is a growing interest in the use of insects for human consumption. Known as entomophagy, this practice offers a plethora of environmental, health and economic benefits. This post aims to explore the possible role insects could serve in the future of sustainable cooking and diets.
Why Entomophagy?
Farming insects for human consumption is considered efficient and environmentally-friendly, compared to the traditional agriculture of raising livestock. Insects reproduce rapidly, suggesting a potential solution for global food scarcity. They emit less greenhouse gases and require less water and land than traditional livestock, making them a far more sustainable food source. Furthermore, insects are a nutrition powerhouse packed with protein, fiber, vitamins, and minerals.
The Challenges Ahead
Despite the numerous positive factors, there are a few obstacles to the widespread adoption of insect consumption. Cultural bias in western societies, legal restrictions, and the lack of culinary tradition are among the most significant challenges. Moreover, ethical considerations related to insects' capacity for pain and suffering need more research and should be addressed.
Commonly Consumed Insects
Crickets, mealworms, and beetles are among the most common insect species consumed worldwide. These insects can be ground into flour, protein bars, bread, pasta and even used in fine dining.
How Are Insects Farmed Sustainably?
Insect farming requires far less water and land compared to traditional animal farming. They can be raised on organic waste materials, contributing significantly to waste reduction and circular economy concepts.
Companies Incorporating Insects in Food Production
Several companies are already pioneering in this space. Bugfoundation uses buffalo worms for creating a nutritious and environmentally-friendly burger. Entomo Farms specializes in producing cricket and mealworm flour. Their products are perceived positively as a sustainable, high-protein alternative in diets.
Insect Consumption In Different Cultures
In many Asian, African, and Latin American cultures, the consumption of insects is a longstanding tradition. In Thailand, edible insects like silkworms and crickets are commonly found in vibrant street markets.
In conclusion, societal and cultural perceptions regarding insect consumption need to shift to harness the benefits offered by this sustainable practice. As the global population continues to rise, introducing innovative, nutrient-rich and sustainable food sources like insects could be a key solution for future dietary challenges.















Comments
Leave a Comment