Mental Health and Gut Health: An Intricate Relationship
Many may find it surprising that there is a closely connected relationship between our guts and our mental health. This relationship is driven by fundamental biological processes, including the gut-brain axis, nervous systems, gut microbiota, and various hormones. This extensive study will discuss these processes in detail and explore the recent studies concerning the direct effects of gut health on mental states like anxiety or depression.
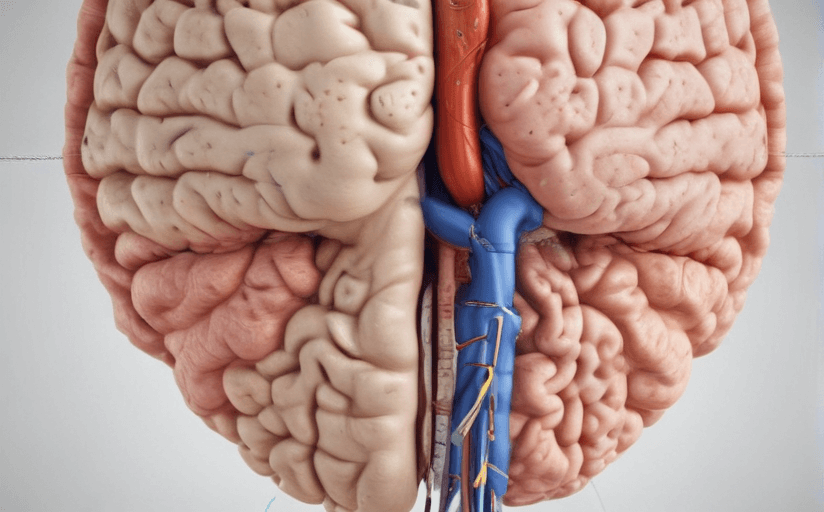
The Role of Gut-Brain Axis
The gut-brain axis refers to the communication system between your gut and brain. It involves complex bi-directional communication circuits between the brain and gut, including neural, hormonal, and immune pathways. Dysregulation of the gut-brain axis is implicated in numerous mental health disorders, including anxiety and depression.
The Impact of Gut Microbiota and Nervous System
The gut is inhabited by trillions of microorganisms known as the gut microbiota. They play a vital role in maintaining the gut's health and communicating with the brain via the gut-brain axis. Unevenness in the gut microbiota, known as dysbiosis, has direct correlations to mental health issues. Furthermore, the enteric nervous system - often referred to as our second brain, has about 100 million nerve cells lining our gastrointestinal tract. It plays a substantial role in this interrelation.
Recent Study Analysis
Recent studies suggest that the health of our gut can impact mental states. For example, dysbiosis can worsen mental health due to the increase of inflammatory responses and alteration of brain chemistry.
In a 2019 study published in the journal 'Gut', it was observed that patients who took probiotics showed improvements in anxiety levels.
Nutrition, Probiotics, and Prebiotics
A balanced diet is crucial for gut health, and it indirectly affects mental well-being. Nutrition influences the composition of gut microbiota, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria. Fermented foods, fibre-rich foods, and omega-3 fats are known to nourish our gut health. Probiotics and prebiotics, either through diet or supplements, also provide immense benefits. They aid in increasing the diversity and abundance of beneficial gut bacteria, thus potentially reducing the symptoms of some mental health disorders.
Conclusion
The intricate relationship between mental health and gut health is so substantial that the gut is often referred to as the second brain. Understanding this link has presented potential therapeutic strategies utilizing the principles of nutrition, probiotics, and prebiotics.









Comments
Leave a Comment